arviz.plot_compare#
- arviz.plot_compare(comp_df, insample_dev=False, plot_standard_error=True, plot_ic_diff=True, order_by_rank=True, legend=True, title=True, figsize=None, textsize=None, labeller=None, plot_kwargs=None, ax=None, backend=None, backend_kwargs=None, show=None)[source]#
Summary plot for model comparison.
Models are compared based on their expected log pointwise predictive density (ELPD). This plot is in the style of the one used in [2]. Chapter 6 in the first edition or 7 in the second.
- Parameters:
- comp_df
pandas.DataFrame Result of the
arviz.compare()method.- insample_devbool, default
False Plot in-sample ELPD, that is the value of the information criteria without the penalization given by the effective number of parameters (p_loo or p_waic).
- plot_standard_errorbool, default
True Plot the standard error of the ELPD.
- plot_ic_diffbool, default
True Plot standard error of the difference in ELPD between each model and the top-ranked model.
- order_by_rankbool, default
True If True ensure the best model is used as reference.
- legendbool, default
True Add legend to figure.
- figsize(
float,float), optional If
None, size is (6, num of models) inches.- titlebool, default
True Show a tittle with a description of how to interpret the plot.
- textsize
float, optional Text size scaling factor for labels, titles and lines. If
Noneit will be autoscaled based onfigsize.- labellerLabeller, optional
Class providing the method
make_label_vertto generate the labels in the plot titles. Read the Label guide for more details and usage examples.- plot_kwargs
dict, optional Optional arguments for plot elements. Currently accepts ‘color_ic’, ‘marker_ic’, ‘color_insample_dev’, ‘marker_insample_dev’, ‘color_dse’, ‘marker_dse’, ‘ls_min_ic’ ‘color_ls_min_ic’, ‘fontsize’
- ax
matplotlib AxesorBokeh Figure, optional Matplotlib axes or bokeh figure.
- backend{“matplotlib”, “bokeh”}, default “matplotlib”
Select plotting backend.
- backend_kwargsbool, optional
These are kwargs specific to the backend being used, passed to
matplotlib.pyplot.subplots()orbokeh.plotting.figure. For additional documentation check the plotting method of the backend.- showbool, optional
Call backend show function.
- comp_df
- Returns:
- axes
matplotlib AxesorBokeh Figure
- axes
See also
Notes
The ELPD is estimated either by Pareto smoothed importance sampling leave-one-out cross-validation (LOO) or using the widely applicable information criterion (WAIC). We recommend LOO in line with the work presented by [1].
References
[1]Vehtari et al. (2016). Practical Bayesian model evaluation using leave-one-out cross-validation and WAIC https://arxiv.org/abs/1507.04544
[2]McElreath R. (2022). Statistical Rethinking A Bayesian Course with Examples in R and Stan, Second edition, CRC Press.
Examples
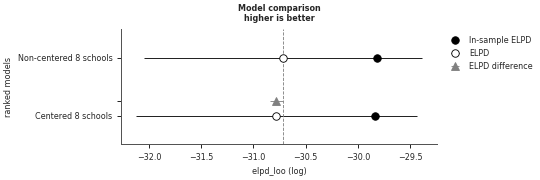
Show default compare plot
>>> import arviz as az >>> model_compare = az.compare({'Centered 8 schools': az.load_arviz_data('centered_eight'), >>> 'Non-centered 8 schools': az.load_arviz_data('non_centered_eight')}) >>> az.plot_compare(model_compare)
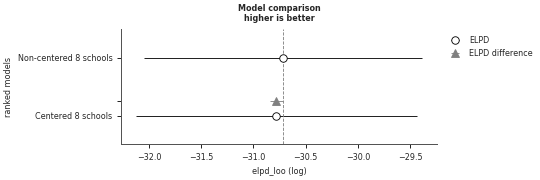
Include the in-sample ELDP
>>> az.plot_compare(model_compare, insample_dev=True)