arviz.plot_ecdf#
- arviz.plot_ecdf(values, values2=None, cdf=None, difference=False, pit=False, confidence_bands=None, pointwise=False, npoints=100, num_trials=500, fpr=0.05, figsize=None, fill_band=True, plot_kwargs=None, fill_kwargs=None, plot_outline_kwargs=None, ax=None, show=None, backend=None, backend_kwargs=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot ECDF or ECDF-Difference Plot with Confidence bands.
Plots of the empirical CDF estimates of an array. When
values2argument is provided, the two empirical CDFs are overlaid with the distribution ofvalueson top (in a darker shade) and confidence bands in a more transparent shade. Optionally, the difference between the two empirical CDFs can be computed, and the PIT for a single dataset or a comparison between two samples.- Parameters:
- valuesarray_like
Values to plot from an unknown continuous or discrete distribution.
- values2array_like, optional
Values to compare to the original sample.
- cdf
callable(), optional Cumulative distribution function of the distribution to compare the original sample. The function must take as input a numpy array of draws from the distribution.
- differencebool, default
False If True then plot ECDF-difference plot otherwise ECDF plot.
- pitbool, default
False If True plots the ECDF or ECDF-diff of PIT of sample.
- confidence_bandsbool, default
None If True plots the simultaneous or pointwise confidence bands with
1 - fprconfidence level.- pointwisebool, default
False If True plots pointwise confidence bands otherwise simultaneous bands.
- npoints
int, default 100 This denotes the granularity size of our plot i.e the number of evaluation points for the ecdf or ecdf-difference plots.
- num_trials
int, default 500 The number of random ECDFs to generate for constructing simultaneous confidence bands.
- fpr
float, default 0.05 The type I error rate s.t
1 - fprdenotes the confidence level of bands.- figsize(float,float), optional
Figure size. If
Noneit will be defined automatically.- fill_bandbool, default
True If True it fills in between to mark the area inside the confidence interval. Otherwise, plot the border lines.
- plot_kwargs
dict, optional Additional kwargs passed to
matplotlib.pyplot.step()orbokeh.plotting.figure.step()- fill_kwargs
dict, optional Additional kwargs passed to
matplotlib.pyplot.fill_between()orbokeh:bokeh.plotting.Figure.varea()- plot_outline_kwargs
dict, optional Additional kwargs passed to
matplotlib.axes.Axes.plot()orbokeh:bokeh.plotting.Figure.line()- ax :axes, optional
Matplotlib axes or bokeh figures.
- showbool, optional
Call backend show function.
- backend{“matplotlib”, “bokeh”}, default “matplotlib”
Select plotting backend.
- backend_kwargs
dict, optional These are kwargs specific to the backend being used, passed to
matplotlib.pyplot.subplots()orbokeh.plotting.figure. For additional documentation check the plotting method of the backend.
- Returns:
- axes
matplotlib AxesorBokeh Figure
- axes
Notes
This plot computes the confidence bands with the simulated based algorithm presented in [1].
References
[1]Säilynoja, T., Bürkner, P.C. and Vehtari, A., 2021. Graphical Test for Discrete Uniformity and its Applications in Goodness of Fit Evaluation and Multiple Sample Comparison. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.10522.
Examples
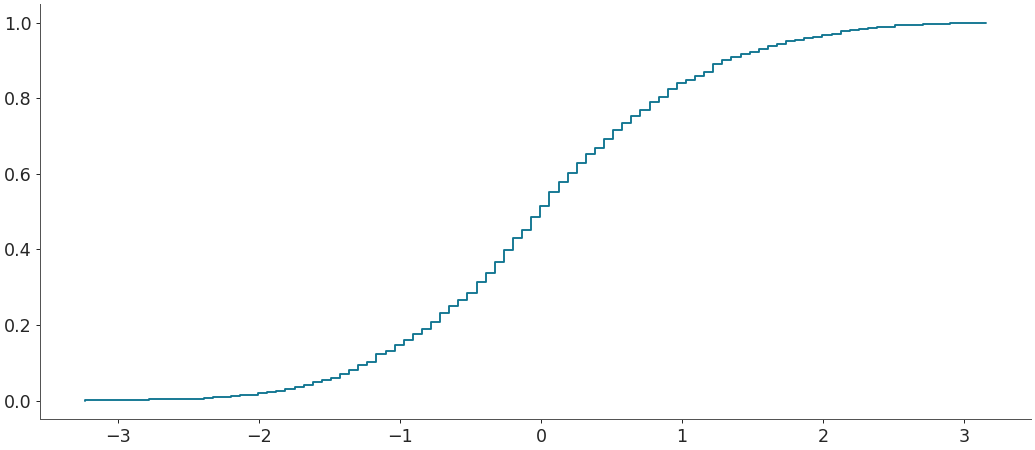
Plot ecdf plot for a given sample
>>> import arviz as az >>> from scipy.stats import uniform, binom, norm
>>> sample = norm(0,1).rvs(1000) >>> az.plot_ecdf(sample)
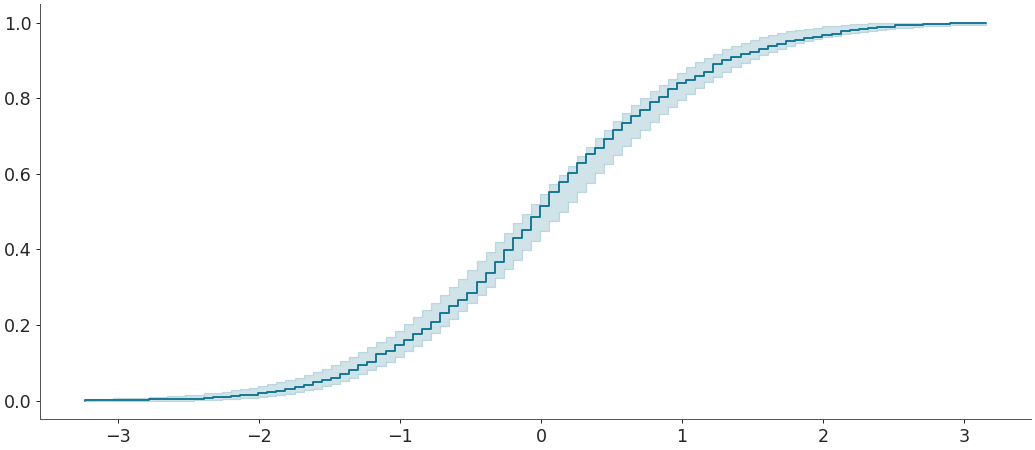
Plot ecdf plot with confidence bands for comparing a given sample w.r.t a given distribution
>>> distribution = norm(0,1) >>> az.plot_ecdf(sample, cdf = distribution.cdf, confidence_bands = True)
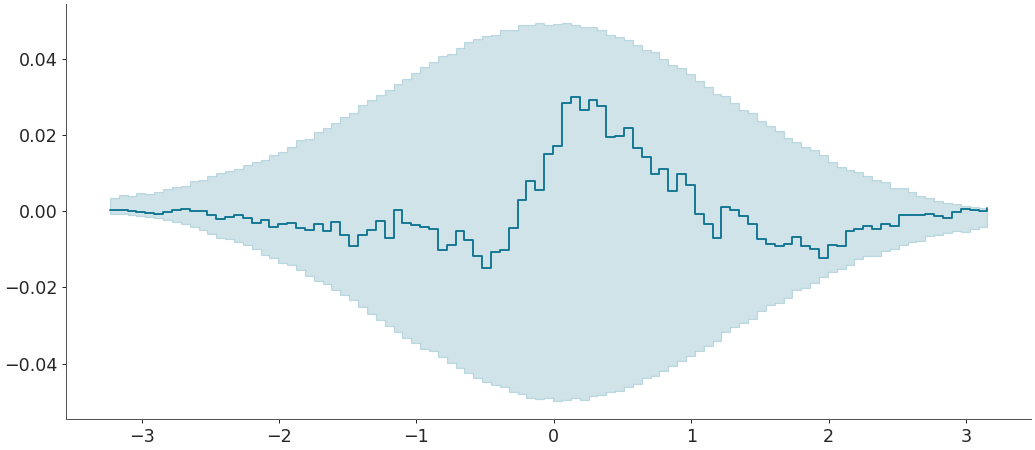
Plot ecdf-difference plot with confidence bands for comparing a given sample w.r.t a given distribution
>>> az.plot_ecdf(sample, cdf = distribution.cdf, >>> confidence_bands = True, difference = True)
Plot ecdf plot with confidence bands for PIT of sample for comparing a given sample w.r.t a given distribution
>>> az.plot_ecdf(sample, cdf = distribution.cdf, >>> confidence_bands = True, pit = True)
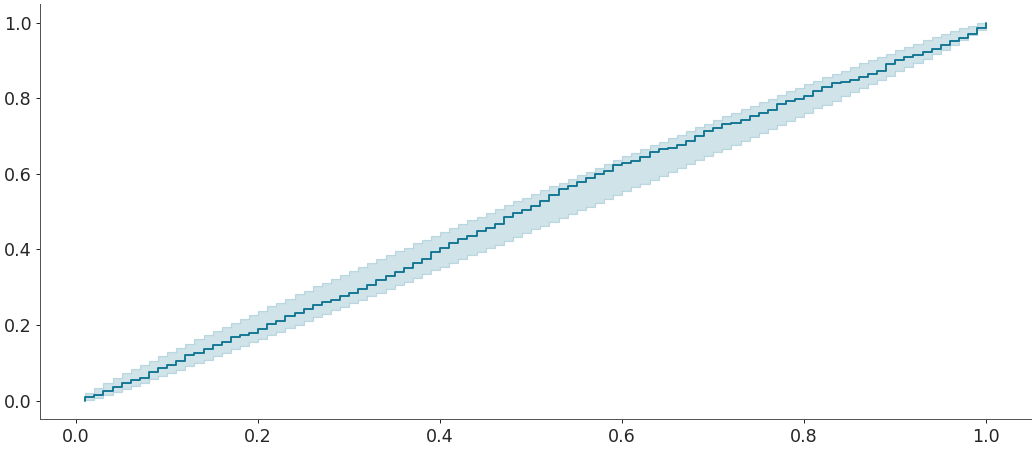
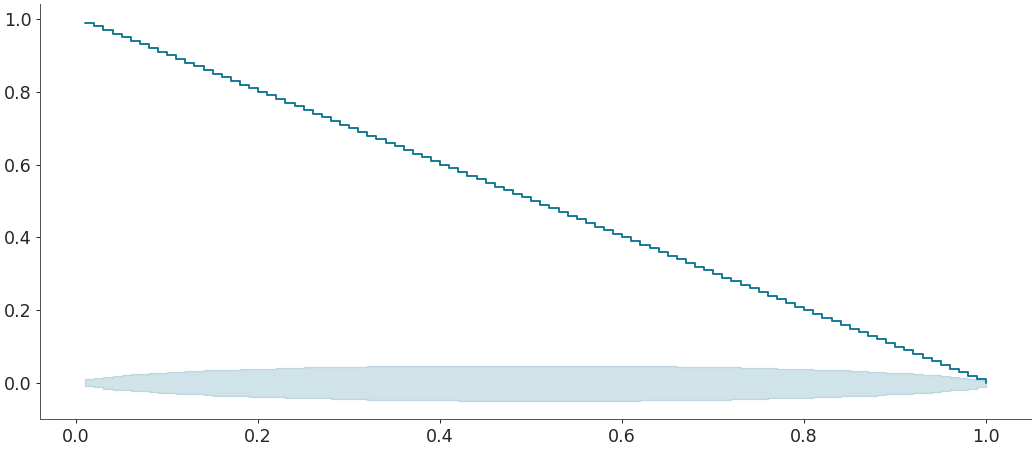
Plot ecdf-difference plot with confidence bands for PIT of sample for comparing a given sample w.r.t a given distribution
>>> az.plot_ecdf(sample, cdf = distribution.cdf, >>> confidence_bands = True, difference = True, pit = True)
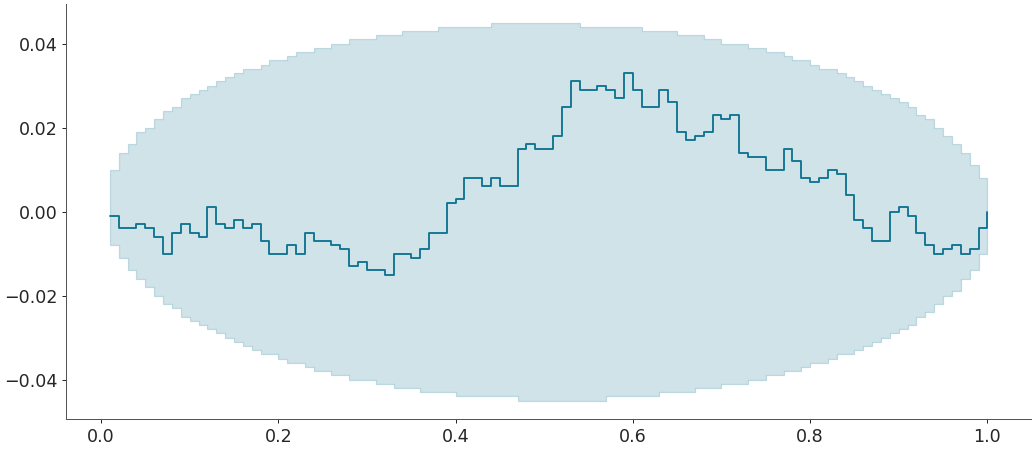
You could also plot the above w.r.t another sample rather than a given distribution. For eg: Plot ecdf-difference plot with confidence bands for PIT of sample for comparing a given sample w.r.t a given sample
>>> sample2 = norm(0,1).rvs(5000) >>> az.plot_ecdf(sample, sample2, confidence_bands = True, difference = True, pit = True)